Gas and Petrochemical Engineering
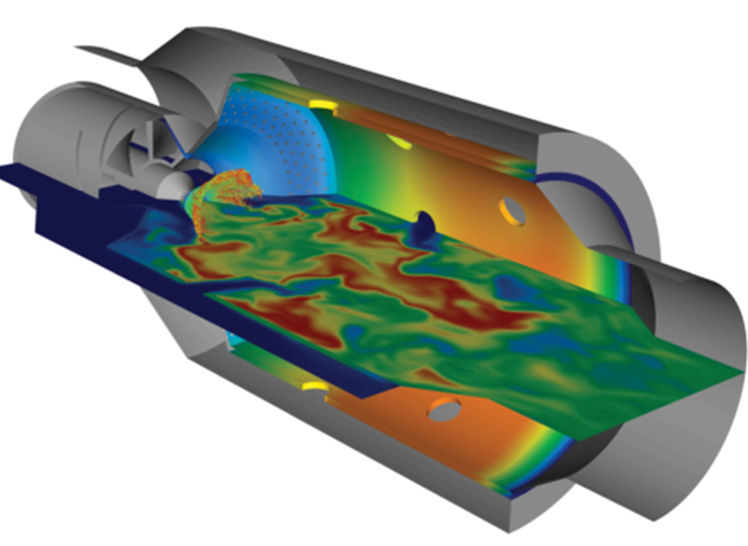
CFD simulations are used in the gas and petrochemical industries to model and analyze fluid flow, heat transfer, chemical reactions, and other related phenomena within a system. The primary purpose of CFD simulations in this field is to better understand and optimize processes, improve design efficiency, and ensure safety and reliability in complex, large-scale operations.
Purpose of CFD Simulations:
In these industries, CFD is particularly useful because it allows engineers to simulate and study processes under a wide range of operating conditions, without the need for expensive and time-consuming physical prototypes or experiments. Some common purposes of CFD in the gas and petrochemical industries include:
Flow Analysis: Predicting and visualizing the movement of gases, liquids, and multiphase fluids within equipment like pipelines, reactors, compressors, separators, and storage tanks.
Heat Transfer Analysis: Understanding how heat moves through systems, optimizing heat exchangers, cooling towers, or reactors to improve thermal efficiency and reduce energy consumption.
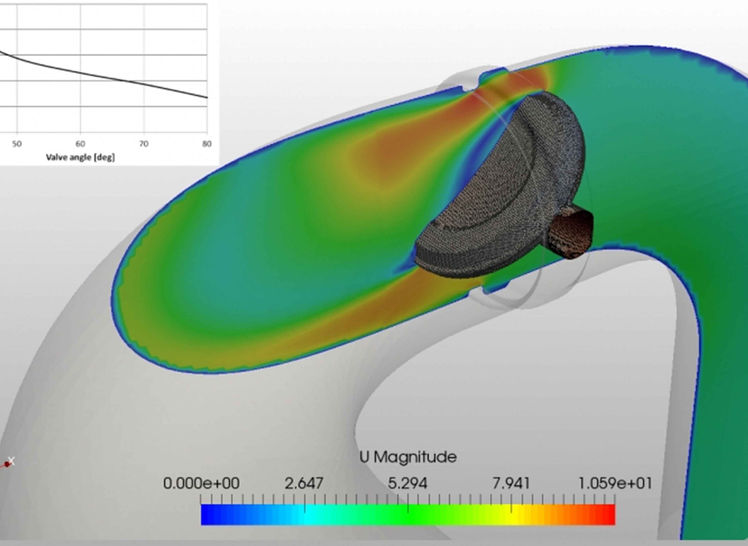
Pressure Drop and Flow Distribution: Calculating pressure losses across equipment and identifying inefficient or non-uniform flow paths, which helps in optimizing pipe designs, compressor performance, and reactor efficiency.
Optimization of Reactors and Catalysts: Modeling chemical reactions inside reactors to optimize reactor performance, enhance yield, and reduce waste by simulating the behavior of fluid mixing, temperature profiles, and reactant conversion.
Safety Simulations: Assessing hazardous scenarios like gas leaks, fire explosions, or pressure vessel rupture, helping to identify potential risks and implement safety measures.
Design Improvements: Simulating the behavior of gases and liquids under different conditions, facilitating the optimization of equipment designs such as heat exchangers, distillation columns, and scrubbers.
Applications of CFD in Gas and Petrochemical Engineering:
Pipeline and Pipeline Network Design:
CFD simulations are extensively used to design and analyze pipeline networks for transporting gases and liquids. It helps in understanding the impact of flow patterns, temperature, and pressure drop, allowing engineers to optimize pipeline layouts for energy efficiency and minimize risk factors such as blockages, corrosion, or leaks.
Heat Exchangers and Heat Transfer Equipment:
CFD is used to design heat exchangers, reactors, and cooling systems by modeling the temperature and fluid flow fields within the system. This ensures efficient heat transfer and energy use while minimizing maintenance and downtime.
Reactor Design and Optimization:
CFD simulations allow for the detailed study of reaction kinetics, flow regimes, and temperature gradients within reactors, leading to more efficient chemical processes. This includes optimizing mixing, minimizing dead zones, and controlling temperature to improve reaction rates and yield.
Gas Separation and Scrubber Design:
CFD simulations are used in the design of gas separation processes like absorption, adsorption, and distillation columns, as well as scrubbers. By modeling gas flow and mass transfer within these units, engineers can optimize their designs to enhance separation efficiency.
Burner and Combustion Process Optimization:
In processes like natural gas combustion, CFD can simulate combustion chambers to model flame propagation, heat release, and exhaust gas emissions. This helps in designing more efficient and environmentally friendly burners for furnaces, boilers, and other combustion devices.
Flow Assurance in Offshore and Subsea Pipelines:
In offshore gas and petrochemical operations, CFD simulations help in solving issues related to the flow of fluids in deep-sea pipelines. Issues like hydrate formation, slug flow, and wax deposition are modeled to ensure that the pipeline can carry the fluids efficiently without blockages or failures.
Benefits of CFD Simulations in Gas and Petrochemical Engineering:
Cost Savings:
CFD reduces the need for physical prototypes and testing, significantly lowering the costs associated with trial-and-error approaches and experimental setups.
By optimizing designs and identifying issues early in the process, companies can avoid expensive redesigns or operational inefficiencies.
Enhanced Efficiency and Optimization:
CFD allows for the detailed analysis of flow dynamics and thermal profiles, leading to better optimization of processes, energy consumption, and overall plant efficiency.
Optimal design and operation of equipment like heat exchangers, compressors, and reactors lead to better energy efficiency and reduced operational costs.
Improved Safety:
Safety is critical in the gas and petrochemical industries due to the high-risk nature of the operations. CFD helps in simulating hazardous scenarios, such as gas leaks, fires, and explosions, to evaluate risk and design systems with higher safety margins.
By evaluating the behavior of fluids under various conditions, engineers can identify potential safety hazards and take preventive actions.
Faster Time-to-Market:
CFD simulations can reduce the development time of new processes or equipment by allowing engineers to virtually test and optimize designs before implementation, leading to quicker production and deployment in the field.
Environmental Benefits:
By optimizing chemical processes and improving combustion efficiency, CFD can help reduce emissions and minimize the environmental impact of gas and petrochemical operations.
Optimized designs for energy efficiency can also lead to a reduction in overall energy consumption, benefiting both the environment and operational costs.
Design Flexibility:
CFD provides engineers with a tool to modify and test a wide range of design parameters quickly. They can explore different configurations or scenarios (e.g., different flow rates, temperatures, or chemical compositions) without physically altering the equipment or processes.
Better Decision-Making:
The visualization capabilities of CFD provide valuable insights into the internal workings of systems, allowing engineers and decision-makers to make more informed choices regarding design, operation, and process optimization.
Predictive Maintenance:
CFD simulations can help predict and detect operational issues such as wear, fouling, or scaling in equipment by simulating how fluids interact with surfaces over time. This allows for more proactive maintenance planning, reducing downtime and extending the life of the equipment.
Conclusion
In summary, CFD simulations offer immense value to the gas and petrochemical industries by enhancing operational efficiency, reducing costs, improving safety, and optimizing designs. The ability to model and analyze complex systems in a virtual environment is a powerful tool that drives innovation and process improvements in this high-stakes sector.