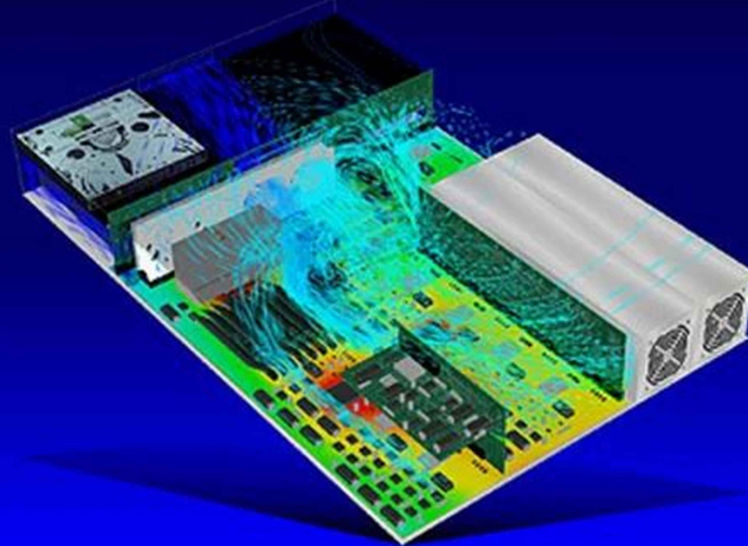
Electronics and Semiconductor Engineering
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations are essential tools for the electronics and semiconductor industries, offering a wide range of applications and benefits. These industries, where precise control of heat and airflow is crucial for performance and reliability, rely on CFD to optimize product designs, manufacturing processes, and system efficiency.
Purpose of CFD Simulations in Electronics and Semiconductor Industry
Thermal Management: One of the primary purposes of CFD simulations in electronics is to model and analyze the heat distribution and thermal behavior in components such as processors, integrated circuits (ICs), power electronics, and semiconductor devices. Proper thermal management is critical in preventing overheating, improving reliability, and ensuring long-term performance.
Airflow and Cooling Systems Design: In the semiconductor industry, cooling is vital due to the high power densities of components like CPUs, GPUs, and chips. CFD simulations help design and optimize air cooling, liquid cooling, and heat sink systems to ensure adequate heat dissipation.
Optimizing Chip Packaging: CFD is used to simulate the flow of air, liquids, or gases within and around semiconductor devices and packaging. This is particularly important in ensuring that the packaging design efficiently cools the chip, avoiding thermal hotspots that can lead to failure.
Electromagnetic Heating Effects: As electronic components, particularly in the RF (radio frequency) and power sectors, become increasingly compact, CFD simulations are used to analyze electromagnetic fields and their heating effects on materials. This is crucial for components such as antennas and microchips.
Design of Clean Rooms and Manufacturing Environments: CFD is used to model airflow in semiconductor clean rooms and manufacturing environments. Effective airflow design prevents contamination, regulates temperature, and ensures a stable and safe production environment.
Applications of CFD Simulations in Electronics and Semiconductor Industry
Thermal Simulation for Power Electronics: Power electronics, such as power supplies, voltage regulators, and energy storage systems, generate significant heat. CFD simulations allow engineers to study heat distribution and optimize the design of heat sinks, cooling channels, and thermal interface materials.
Chip Cooling: With the rising demand for miniaturized, high-performance devices, semiconductor chips require efficient cooling. CFD simulates air or liquid flows around chips and identifies the best cooling methods to prevent thermal failure.
High-Density Integrated Circuits (ICs): As integrated circuits become more densely packed, managing the heat generated by these systems is increasingly difficult. CFD simulations help model the cooling solutions for ICs, improving the performance and lifespan of these complex devices.
Flow Modeling for Semiconductor Manufacturing: In semiconductor fabrication, processes like etching, deposition, and wafer cleaning depend on precise fluid flows. CFD can model these fluid dynamics, optimizing the process, ensuring uniformity, and reducing the potential for defects.
Data Centers: In data centers, the heat generated by thousands of servers needs to be effectively managed to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the equipment. CFD simulations can help design the airflow and cooling systems to maintain the ideal thermal environment.
Benefits of CFD Simulations in Electronics and Semiconductor Industry
Enhanced Product Reliability and Performance: CFD allows engineers to identify and mitigate potential thermal issues before physical prototypes are built. By understanding how heat affects a device’s performance, companies can design products that operate more reliably and efficiently, avoiding costly failures.
Cost Reduction: CFD simulations can help reduce physical testing and prototyping costs. By predicting how different designs will behave in real-world conditions, it minimizes the number of prototypes needed and accelerates product development cycles.
Faster Time to Market: By enabling faster identification of design flaws and inefficiencies, CFD simulations reduce the time required to develop and finalize products. This leads to quicker turnaround times and allows manufacturers to meet market demand more swiftly.
Optimized Cooling Solutions: CFD simulations help optimize cooling systems, which are vital for the performance and longevity of electronic devices. This leads to more efficient products and reduced energy consumption, which is a growing concern in both consumer electronics and industrial applications.
Energy Efficiency: By simulating various cooling methods and thermal management strategies, CFD helps identify the most energy-efficient solutions for thermal regulation, reducing the overall energy consumption of devices and systems.
Minimized Downtime: Proper thermal management is essential for the prevention of overheating, which can lead to system failures or downtime. CFD allows for better planning and optimization of thermal systems, ensuring that devices perform consistently without unexpected disruptions.
Improved Design Innovation: With CFD, engineers have the ability to test innovative designs under virtual conditions. This helps in the exploration of unconventional and new ideas that may have been previously difficult or too costly to prototype and test in real life.
Regulatory Compliance: In industries like semiconductors, where product reliability and safety are crucial, CFD simulations assist in ensuring that designs comply with industry standards and regulations related to heat management, airflow, and energy efficiency.
Conclusion
CFD simulations offer transformative benefits to the electronics and semiconductor industries by optimizing thermal management, enhancing performance, and reducing costs. From power electronics and chip cooling to the design of clean rooms, CFD provides invaluable insights that improve the design, manufacturing, and operation of complex electronic systems. As devices become more powerful and compact, the role of CFD in ensuring reliability, performance, and energy efficiency will only continue to grow.