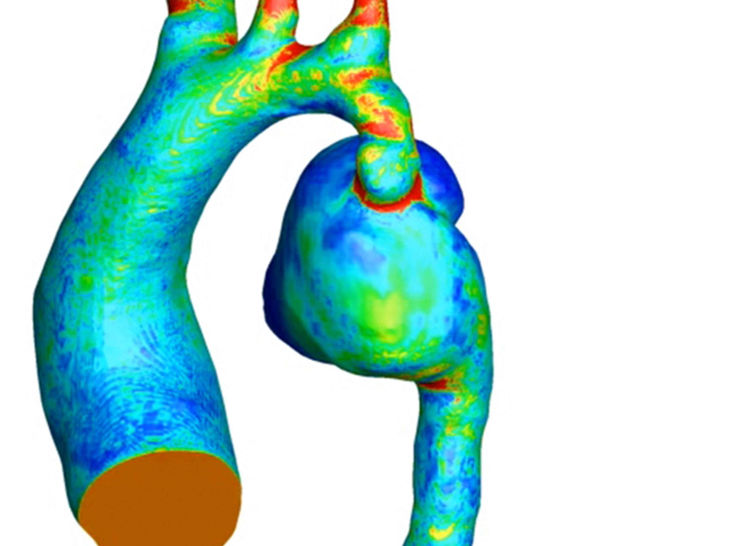
Biomedical Engineering
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations play a crucial role in the biomedical engineering industry, particularly in the design and optimization of medical devices, diagnostic tools, and treatments that involve fluid flow. The application of CFD allows for detailed analysis of complex fluid behavior in various biomedical contexts without the need for costly and time-consuming physical testing. Here’s an overview of the purpose, application, and benefits of CFD simulations in the biomedical field:
Purpose of CFD Simulations in Biomedical Engineering
Understanding Fluid-Structure Interactions: In many biomedical applications, fluid flow interacts with biological tissues and structures (e.g., blood flow in arteries or airflow in the lungs). CFD helps simulate and study these interactions, providing insights into how fluids behave under different conditions and how they affect surrounding tissues.
Improving Medical Device Design: CFD is used to design and optimize medical devices that deal with fluid flow, such as heart valves, stents, blood pumps, and inhalers. By simulating the fluid dynamics, engineers can test prototypes virtually, optimizing performance before physical models are created.
Enhancing Diagnostic Tools: CFD can model the flow of blood, air, or other fluids in the human body, assisting in the design of diagnostic tools like MRI, CT scanners, and ultrasound systems. This helps in understanding how devices interact with human systems, improving the accuracy of diagnoses.
Personalized Medicine: CFD simulations can help tailor medical treatments to individual patients by simulating the patient’s unique anatomy. This can be especially important in surgeries or treatments involving complex fluid flows, like cardiovascular interventions or respiratory therapies.
Applications of CFD Simulations in Biomedical Engineering
Cardiovascular Studies:
Blood Flow Analysis: CFD can simulate blood flow through arteries, veins, and the heart, helping in the design of stents, artificial heart valves, and bypass grafts.
Aneurysm Prediction: By modeling blood flow through vascular networks, CFD can help predict the development of aneurysms, a critical application for early detection and prevention.
Hemodynamics: Understanding the mechanical forces acting on blood vessels and heart tissues can improve the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Respiratory System:
Airflow in Lungs: CFD is used to simulate airflow in the lungs, helping improve the design of ventilators, inhalers, and artificial lung systems.
Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): By modeling airflow in patients with obstructed airways, CFD can assist in designing better therapies and understanding disease progression.
Bioprocessing and Drug Delivery:
Drug Dispersion: CFD is used to model the dispersion of drugs in the bloodstream, which helps in designing more effective drug delivery systems.
Optimizing Medical Devices: In devices like syringes or infusion pumps, CFD can simulate fluid dynamics to optimize their performance, ensuring accurate and efficient drug administration.
Orthopedic and Surgical Simulations:
Bone-Implant Interactions: CFD can model the fluid dynamics between medical implants (such as prosthetics) and surrounding tissues, helping optimize implant design for better integration and performance.
Surgical Planning: Surgeons can use CFD simulations to visualize complex anatomical regions and plan surgeries with greater precision, particularly in the case of tumors, complex vascular structures, or organ transplants.
Benefits of CFD Simulations in Biomedical Engineering
Cost-Effectiveness: CFD simulations reduce the need for physical prototyping and testing, which can be expensive and time-consuming. Virtual testing of designs helps identify potential issues before manufacturing begins, thus saving costs in the development process.
Enhanced Precision and Accuracy: CFD allows for the analysis of detailed and complex fluid dynamics that are difficult to measure physically. This leads to more accurate predictions, better understanding of the biological systems, and improved design choices.
Faster Product Development: With the ability to test numerous scenarios quickly and efficiently through simulations, products such as medical devices or surgical procedures can be developed more rapidly, speeding up time to market.
Customization and Personalization: CFD simulations can model fluid dynamics based on individual patient data, enabling personalized treatment plans. This is especially valuable for conditions like cardiovascular diseases, where a tailored approach can lead to better outcomes.
Improved Patient Outcomes: By using CFD to understand and optimize medical devices and treatments, patients can benefit from more effective interventions. For example, improved stent designs, more efficient drug delivery systems, or better surgical planning can lead to safer, more successful treatments.
Regulatory Approval: CFD simulations provide robust data that can be used to support regulatory filings with agencies like the FDA, demonstrating that devices meet the necessary safety and performance criteria.
Risk Reduction: By virtually testing different conditions, CFD simulations help identify potential issues before they occur in the real world. This reduces the risk of device failure, adverse events, and complications during surgeries.
Conclusion
In summary, CFD simulations are an invaluable tool in the biomedical engineering industry, providing insights that lead to better-designed medical devices, improved treatments, cost savings, and ultimately, enhanced patient care. The ability to model fluid dynamics and biological systems in great detail is transforming how biomedical products are developed, tested, and personalized.